A person’s life has two dentition phases – Primary dentition, i.e. the Deciduous Teeth / Milk teeth and the Permanent Teeth which are seen for the entire lifetime. There are several differences between the Deciduous / Primary and Permanent teeth in the morphology and various other aspects, and it is the deciduous teeth which erupt first, then followed by the permanent teeth. As and when the milk teeth are lost, the permanent teeth start replacing them.
The primary teeth start erupting from the age of 6-7 months, and they grow and finally lost by the age of 11 years, and the permanent teeth start growing from the age of 6-7 years and stay permanently only if they ideally erupt and are maintained well. The last permanent teeth that are erupted in the oral cavity are the Wisdom teeth, i.e. the 3rd molar.
The primary and permanent teeth are not only different externally, but have got several differences in the internal morphology too. A total of 20 deciduous teeth and 32 permanent teeth erupt in the body, i.e. 52 total teeth in the entire lifetime.
The size of the crowns of the primary molar teeth affects the way the permanent dentition and the jaw growth occurs, because if the deciduous molars fall off early and if no proper measures are taken, the permanent molar may drift forward and it could lead to lesser spaces for the eruption of the premolar teeth. While there are a few times when the primary and permanent teeth are present at the same time in the mouth, it is necessary to understand the differences between the two to easily identify the tooth for any treatment planning.
Following are the differences between the Deciduous Teeth and the Permanent Teeth (Check out the differences between Maxillary and Mandibular Incisors in Permanent dentition):
|
Feature |
Deciduous Teeth |
Permanent Teeth |
| Number | 20 teeth in total | 32 teeth in total |
| Types | 2 incisors, 1 canine and 2 molars in each quadrant. There are no premolars. A total of 8 incisors, 4 canines and 8 molars erupt. | 2 incisors, 1 canine, 2 premolars and 3 molars in each quadrant. A total of 8 incisors, 4 canines, 8 premolars and 12 molars erupt. |
| Size | These are the smaller teeth and each tooth is smaller than the permanent successor. Only the Mesiodistal width of primary molar is greater than the Mesiodistal width of the permanent pre-molar. | The permanent teeth are larger than the primary teeth in size, except for the pre-molars which replace the primary molars, with a smaller mesiodistal width. |
| Shape | The cusps are more pointed and the crowns are bulbous. The crowns of incisors and canines are relatively broader. The contact areas are smaller. | The cusps are blunt. The crowns are not bulbous. The contact areas are broader. |
| Colors | Enamel is less translucent, thus the color of the primary teeth is whiter. | Enamel is more translucent and thus the color of the permanent teeth is bluish-white. |
| Cervical Margin | The enamel ends abruptly at the neck. First molars show a bulge near the cervical margin at mesio-buccal region – known as cervical ridge. Necks are short and more constructed. Anteriors show prominent cervical ridge labially and lingually. | The enamel ends gradually. First molars do not have any bulge near cervical margins. Necks are longer and less constricted. |
| Occlusal Area | The Bucco-lingual diameter of molars is narrower because the buccal and lingual surfaces converge. | Buccal and lingual surfaces do not converge and therefore bucco-lingual diameter is wider. |
| Roots | Roots are shorter and delicate though compared to crown size they are relatively longer. The roots separate close to crown. The roots diverge widely. | Roots are longer and strong. In multi-rooted teeth there is a trunk and roots do not diverge close to crown. |
| Pulp Cavity | Dentin is less thick. Pulp cavity is larger and pulp horns rise high in the cuspal region. | Dentin is thicker. Pulp cavity is smaller and pulp horns are lower. |
| Enamel | More permeable, less calcified and shows more attrition. Rods near cervical margin are perpendicular to dentino-enamel junction. | Enamel is less permeable, more calcified and show relatively less attrition. Rods near cervical margin are directed apically. |
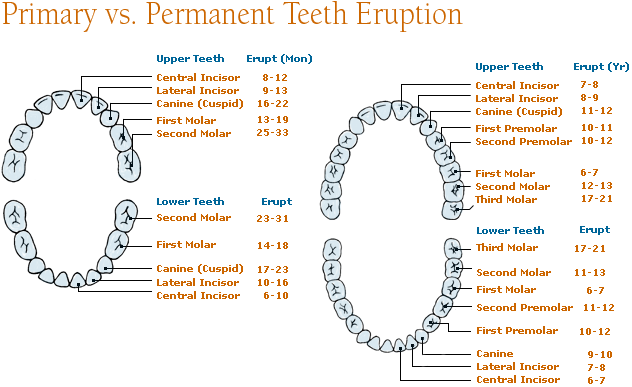
| Eruption | Eruption starts at 6 months and continues till 3 years, and the primary teeth are exfoliated by 13 years. | Eruption starts at 6 years and continues till 25 years or more and stays in oral cavity for a long time. |
| Placement in Jaws | They are set perpendicularly in jaws. | They are placed obliquely in jaws. |
| 1st Upper Molar | 3 Cusps | 4 Cusps |
| 2nd Upper Molar | 4 Cusps | 4 Cusps |
| 1st Lower Molar | 4 Cusps | 5 Cusps |
| 2nd Lower Molar | 5 Cusps | 4 Cusps |
I appreciate it for posting “Differences between Primary Teeth (Milk Teeth) and Permanent Teeth | Dental Articles | Dr.
Chetan”. Imay really be back for far more browsing and writing comments shortly.
I am grateful, Jeffry
thanks you very much !
dental student .
thanks very much I am very interested by u’r post
Thanks, it help us
Thank you very much Dr. Chetan . It is very helpful.
I am very very thankful to you
my son is seven years old and has got his incisors brown and seem damaged or one would say rotten and it looks like they are not going to be replaced like his other teeth so I am worried.
Please advice because they are not paining
This is a very simplified and intelligent presentation. Much gratitude. From a dental student
very nice dr. thank you
thanks
kmt didn’t help me but good info
i want the eruption of the difference of the milk and permanent teeth
fantastic job $ thanks so much
Hi there,
I am a dental hygienist writing an online continuing education class. May I use the images of the eruption of the permanent and primary teeth AND the chart of primary vs permanent teeth.
Thank you
Sure