Alveolar bone(also called as alveolar process) is a part of the jaws which forms and protects the sockets for the teeth. Its the thickened part of the ridge of the jaws.
Maxillary alveolar process is the ridge present on the superior surface, and the mandibular alveolar process is the ridge seen on the inferior surface. The alveolar process is the thickest region in the jaw.
The alveolar process is the bony part and it has 2 parts on its own –
1. Alveolar bone proper
2. Supporting alveolar bone
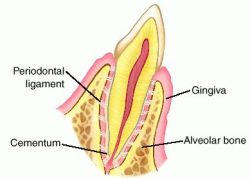 Alveolar bone proper is present just adjacent the tooth socket around the root and it gives the attachment to the periodontal ligament fibers, which are the principle fibers. These fibers which enter the bone are regarded as Sharpey’s fibers. And the bone which is the lodgement site for the fibers is called as the Bundle bone.
Alveolar bone proper is present just adjacent the tooth socket around the root and it gives the attachment to the periodontal ligament fibers, which are the principle fibers. These fibers which enter the bone are regarded as Sharpey’s fibers. And the bone which is the lodgement site for the fibers is called as the Bundle bone.
One more part of the alveolar bone proper is called as the Lamellated bone, where there is normal lamellae structure of a bone with the haversian system.
The alveolar bone proper is also called as “Cribriform plate” due to the presence of perforations and canals for the entry of vessels and nerves.
The supporting alveolar bone has 2 regions –
Cortical bone
Spongy bone
Cortical bone contains cortical plates which have perforations in the anterior teeth, for the entry of blood vessels into the inner parts of the teeth. The cortical plates are least in the maxillary region and the highest are seen in the molar region of the mandibular bone.
Spongy bone, also called as Spongiosa, contains trabeculae. The spongy bone is further divided into 2 types –
a. Type I – Contains trabeculae which are regularly arranged in a ladder like arrangement.
b. Type II – Contains trabeculae in an irregular arrangement.
Type I is more seen in the mandibular alveolar bone, and Type II is more in the maxillary alveolar bone.
thanks for the post 🙂